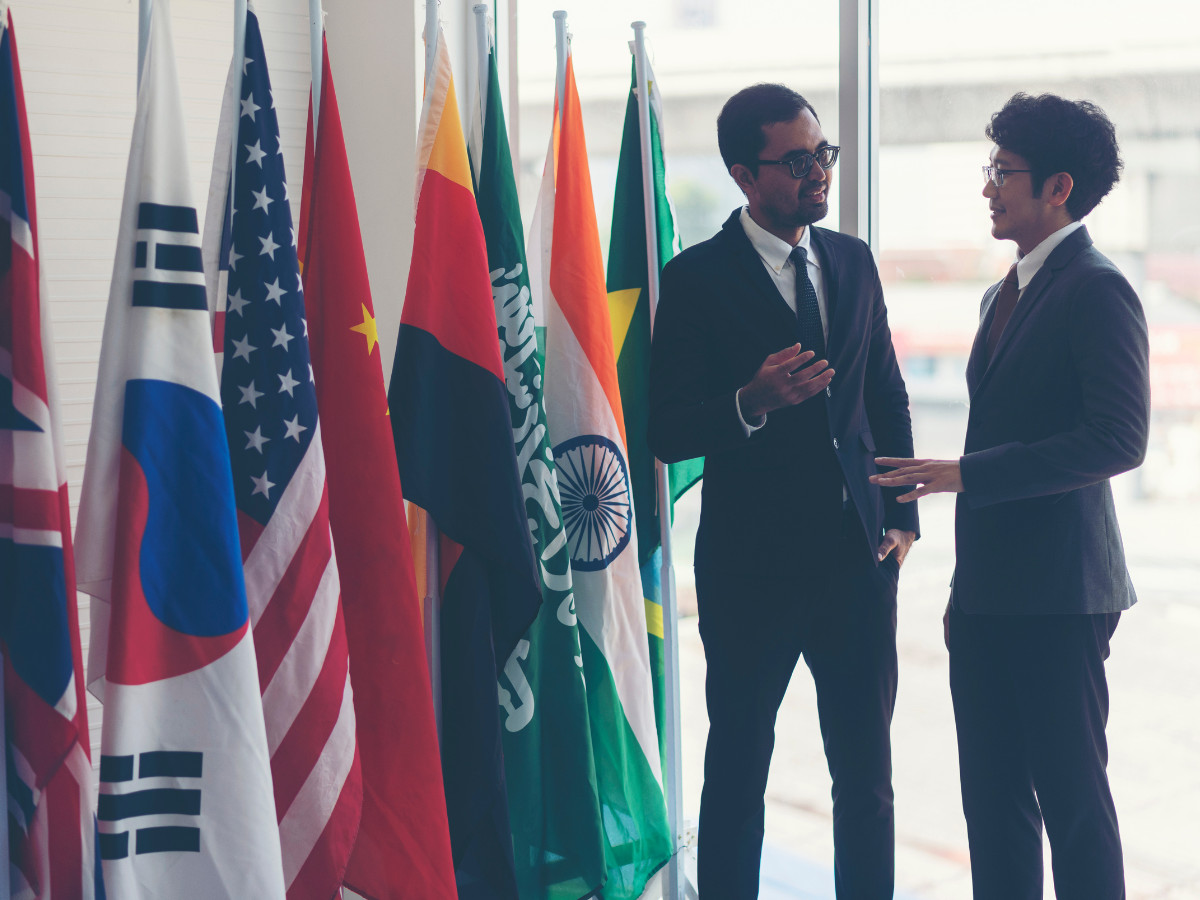
The term “international system” is central to understanding global interactions and international relations. From diplomacy to economic policies, this system forms the foundation for how countries, organizations, and individuals interact across borders. But what exactly is an international system, and how does it shape global politics? Below, we’ll explore its definition, key components, and the dynamic forces that drive the international system forward.
Defining the International System
The international system refers to a network of states, organizations, and individuals that interact on a global stage. It provides the framework that dictates who interacts with whom, how these interactions occur, and what rules govern these relationships. Think of it as the “big picture” of global affairs, encompassing economic ties, military alliances, and cultural exchanges.
At its core, the international system serves as the context within which foreign policies are crafted and international relations are conducted. This system works as a backdrop for cooperation, competition, and, at times, conflict as states work to achieve their goals, maintain security, and protect their interests.
Example in Action
For example, consider climate change negotiations. Countries like the United States, China, and small island nations come together within the framework of the international system to discuss and implement solutions. This kind of interaction showcases how countries tackle collective challenges by engaging in dialogue under shared rules.
The Building Blocks of the International System
To understand the international system, it’s essential to examine its primary components. These building blocks, including states, intergovernmental organizations, and non-state actors, shape the dynamics of international relations.
1. States as Primary Actors
States are the most important players in the international system. Governments control their own territories, make decisions on foreign and domestic policies, and represent their population when dealing with other countries. They engage with one another either directly, through diplomacy, or indirectly, through participation in international organizations.
These relationships can be economic, political, or cultural in nature. States may also form alliances to advance shared goals or maintain a balance of power. For example, NATO (the North Atlantic Treaty Organization) acts as a military alliance where member states agree to collective defense, reflecting how states collaborate within the system.
Example of State Interactions
Trade agreements like the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) are a direct result of state-level interactions. The agreement facilitates mutual economic benefits while also strengthening diplomatic ties.
2. Intergovernmental Organizations (IGOs)
Intergovernmental organizations (IGOs) like the United Nations (UN), World Trade Organization (WTO), and European Union (EU) are essential components of the international system. They act as structured platforms for states to engage with each other and pursue collective goals. These entities provide a framework for cooperation, policymaking, and conflict resolution.
Key Roles Played by IGOs
- Setting Standards and Policies: Organizations like the WTO set trade regulations that member states are expected to follow.
- Mediating Disputes: The UN acts as a mediator in global conflicts, facilitating peaceful resolutions.
- Promoting Global Stability: NATO ensures military collaboration aligned with security goals.
These organizations contribute to global order by addressing complex issues that individual states may struggle to resolve on their own.
3. Non-State Actors
While states and IGOs take center stage, non-state actors also have a significant impact on the international system. These include multinational corporations, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), the media, and even influential individuals. These actors often influence public opinion, enhance international cooperation, and push for global change.
One noteworthy example is Greenpeace, an NGO committed to environmental advocacy. Through global campaigns and negotiations, Greenpeace has played a pivotal role in shaping international policy on issues like climate change and deforestation.
More Examples of Non-State Power
- Corporations like Amazon or Tesla influence international economics and innovation.
- Media Outlets can frame how global events are interpreted, impacting political responses.
The Dynamic Nature of the International System
The system is not static. It shifts and evolves as globalization and new challenges transform international relations. Factors like emerging powers, technological innovation, and global crises—as seen during the COVID-19 pandemic or the ongoing energy crisis due to war in Ukraine—constantly reshape the system.
Global Examples of Change
- Power Shifts
The rise of China as an economic and military power exemplifies how the dynamics of the international system evolve. Countries must adapt their foreign policies to adjust to such shifts in influence. - Tech Disruption
Digital advancements, such as AI and space exploration, are creating new domains for international cooperation and competition. - Collective Action
Global crises like climate change show how the international system fosters collaboration. Agreements like the Paris Accord bring hundreds of states together to work toward shared environmental goals.
Join the Immerse Education 2025 Essay Competition
Follow the instructions to write and submit your best essay for a chance to be awarded a 100% scholarship.

Why the International System Matters in International Relations
International relations, at its heart, focuses on how countries and other global actors work together to maintain peace, promote prosperity, and address global issues. The system provides the foundation for these interactions, ensuring there’s a structured approach to diplomacy, conflict resolution, and economic policy.
Without this system, international relations would lack the consistency and predictability that are essential for managing global challenges. For example, treaties like the Geneva Conventions, which outline the rules of war, depend on the international system for their implementation and enforcement.
Final Thoughts
The international system is a complex network that defines how the world works on a global scale. It brings together states, organizations, and individuals in a dynamic, evolving structure. Whether discussing trade agreements, security alliances, or humanitarian efforts, it shapes the policies and relations essential for global cooperation.
By understanding this framework, we gain deeper insights into international relations, enabling us to better interpret the decisions and actions of major global players.
Whether you’re a student of diplomacy or simply curious about how countries operate in today’s interconnected world, attending summer schools internationally, such as a New York summer school or Sydney summer school can be an excellent way to explore the international system and gain a deeper understanding understanding of these concepts through exposure to diverse perspectives and real-world case studies.
If you’re fascinated by the topic of international relations, check out our international relations summer schools for high school students.